Highlights
- Scalp psoriasis significantly affects quality of life, demanding personalized care and innovative treatments.
- New therapeutic advancements can enhance adherence and effectiveness in managing scalp psoriasis symptoms.
Summary and Overview
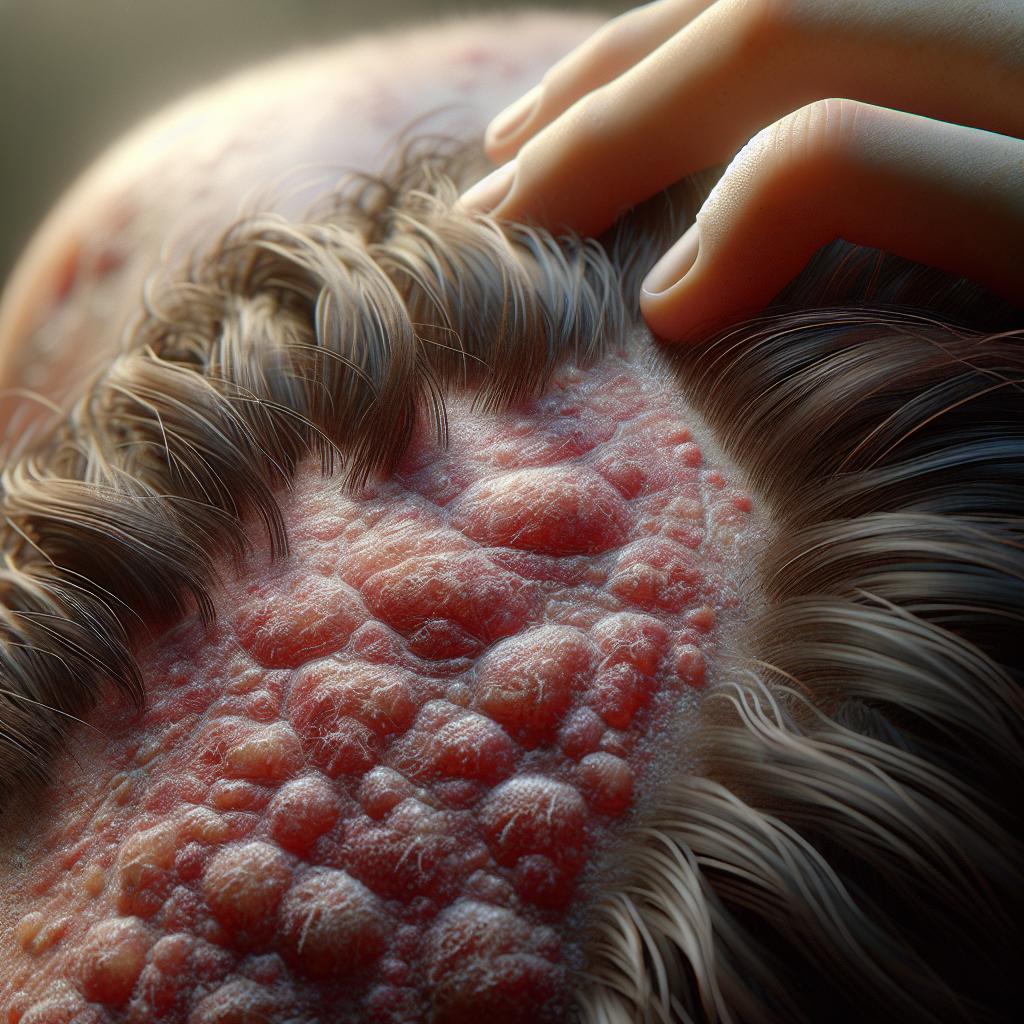
Scalp psoriasis is a common, chronic inflammatory skin disorder marked by erythematous, scaly plaques on the scalp, affecting nearly half of psoriasis patients. It arises from genetic, immunologic, and environmental factors, causing itching, visible scaling, and significant psychosocial distress. The condition is more prevalent in wealthier, temperate regions, with lifestyle factors like smoking and obesity worsening severity.
Management is challenging due to hair interference and disease recurrence. Treatments include topical corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, phototherapy, and systemic biologics targeting immune pathways. New topical agents and small molecule inhibitors improve efficacy and adherence, though cost and side effects remain barriers. Early, aggressive treatment of scalp involvement is emphasized to reduce physical and psychological impacts. Research gaps exist in underrepresented regions and standardized outcomes, necessitating large-scale international studies.
Epidemiology
Psoriasis incidence and prevalence vary by age, sex, geography, and socioeconomic status, with Europe showing the highest rates and Africa the lowest. Globally, 2019 estimates included 4.6 million new cases and over 40 million existing cases. Onset peaks occur between 18–39 and 50–79 years, with slight sex differences. Higher burden correlates with wealthier countries, overweight populations, and behavioral factors like smoking. Healthcare access varies regionally, with North America showing lower consultation rates despite high disease burden.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis relies mainly on clinical examination of well-defined red plaques with silvery scales on the scalp, sometimes extending beyond hairlines. Trichoscopy aids differentiation by identifying characteristic vascular patterns. In uncertain cases, biopsy reveals typical histopathological features. Differential diagnoses include seborrheic dermatitis, tinea capitis, and lichen planopilaris, which differ in lesion appearance and require distinct treatments.
Treatment
Scalp psoriasis treatment is complicated by hair presence and quality of life impact, necessitating individualized regimens.
Phototherapy
UV light therapy, including UVB and targeted laser treatments, effectively reduces symptoms and can be administered in clinics or at home.
Topical Treatments
Topical corticosteroids combined with vitamin D analogs remain the mainstay, with newer foams, shampoos, and sprays enhancing adherence. Coal tar shampoos, vitamin A derivatives, and emerging agents like roflumilast and tapinarof offer additional options, though cosmetic concerns and application challenges affect use.
Systemic and Biologic Therapies
For moderate to severe or refractory cases, biologics targeting IL-17 and IL-23 pathways, small molecule inhibitors, and traditional systemic agents like methotrexate are effective but limited by side effects, resistance, and cost.
Future Directions
Research focuses on novel biologics, small molecule inhibitors, combination therapies, and improved topical delivery systems to enhance efficacy, safety, and patient adherence.
Recent Trends and Advances
FDA approval of roflumilast foam for scalp psoriasis and pediatric indications for guselkumab highlight therapeutic progress. Improved topical formulations and combination therapies boost adherence and efficacy. Biologics like secukinumab and bimekizumab demonstrate superior outcomes, with ongoing trials to compare agents and refine treatment goals. Consensus increasingly supports early systemic therapy for scalp involvement due to its disproportionate quality-of-life impact.
Impact on Quality of Life
Scalp psoriasis significantly impairs quality of life by causing stigma, psychological distress, and social avoidance, especially among older adults. The burden is higher in high-income regions with greater prevalence. Even limited scalp disease can profoundly affect self-esteem, underscoring the need for patient-centered treatment approaches and consideration of advanced therapies for high-impact areas.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Effective management combines consistent treatment application, skin hydration, and avoidance of triggers such as scratching, insect bites, skin trauma, stress, and alcohol consumption. Preventive measures and lifestyle modifications help reduce flare frequency and maintain remission.
Research Gaps and Future Directions
Current data are limited by underreporting in some regions and methodological constraints, hindering comprehensive global understanding. Large-scale, standardized international studies, like Project ALL, are needed to improve epidemiological accuracy, capture diverse populations, and inform tailored interventions. Future research should address healthcare access disparities and the broader quality-of-life impact to optimize clinical practice and policy.
The content is provided by Sierra Knightley, Scopewires